Introduction
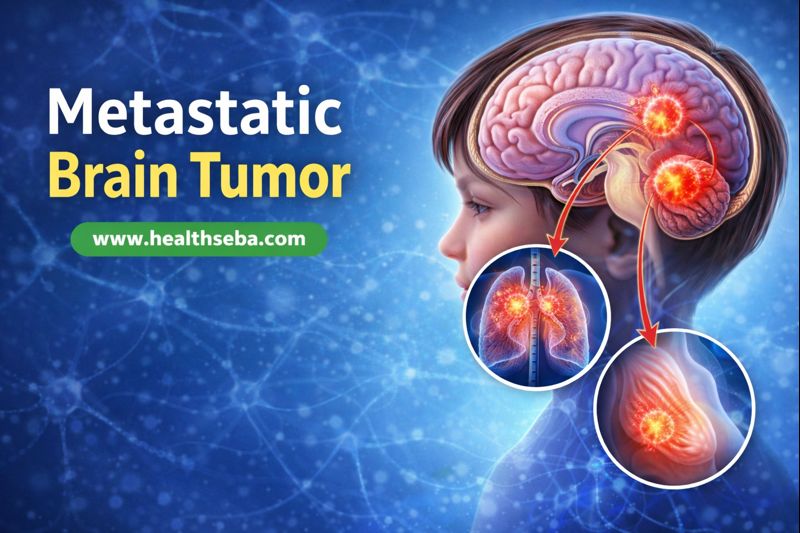
A Metastatic brain tumor develops when cancer cells travel from another part of the body and grow inside the brain. Doctors also call this condition secondary brain cancer. This type of tumor appears more often than primary brain tumors that start in brain tissue. Cancer cells usually spread through the bloodstream and settle in brain tissue, where they begin forming new tumors.
Global Statistics
A Metastatic brain tumor represents the most common brain tumor seen in adults. Studies show that 20–40% of people living with cancer may develop brain metastases during their illness. Lung cancer, breast cancer, melanoma, kidney cancer, and colorectal cancer most frequently spread to the brain. Improved cancer treatments now help patients live longer, which increases the chance of metastasis appearing later.
Causes and Risk Factors
Cancer that spreads from another organ causes a Metastatic brain tumor. Malignant cells break away from the original tumor, enter blood vessels or lymph channels, and travel to the brain. Several cancers carry higher risk:
Lung cancer
Breast cancer
Melanoma (skin cancer)
Kidney cancer
Colon and rectal cancer
Advanced-stage cancers raise the likelihood of brain spread. Delayed diagnosis and incomplete treatment also increase risk.
Symptoms
Symptoms depend on tumor size, number, and location inside the brain. A Metastatic brain tumor often produces noticeable neurological changes. Common warning signs include:
- Persistent or severe headaches
- Seizures in someone with no seizure history
- Nausea or repeated vomiting
- Blurred or double vision
- Memory loss or confusion
- Personality or behavior changes
- Weakness or numbness on one side of the body
- Trouble walking or poor balance
- Sudden neurological symptoms require urgent medical attention.
Types
Doctors classify tumors based on number and location:
Single Brain Metastasis
One tumor appears in the brain.
Multiple Brain Metastases
Several tumors grow at the same time. This pattern occurs most often.
Leptomeningeal Metastasis
Cancer spreads to the fluid and membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord.
Diagnosis
Doctors use advanced imaging and clinical evaluation to confirm a Metastatic brain tumor.
Prevention and Risk Reduction
Doctors cannot fully prevent a Metastatic brain tumor, though early cancer care lowers risk.Helpful steps include:
- Early detection of primary cancers
- Completing recommended cancer treatment
- Regular follow-up scans for cancer survivors
- Avoiding tobacco use
- Reporting new neurological symptoms quickly
- Ongoing monitoring plays a key role in early discovery.
Conclusion
A Metastatic brain tumor signals that cancer has spread and requires urgent, specialized care. Early diagnosis, proper imaging, and advanced treatment approaches help manage symptoms and extend survival. Prompt medical evaluation improves outcomes and supports better quality of life for patients facing this serious condition.
Disclaimer
This article provides general educational information only. It does not replace professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult an oncologist or neurologist for proper evaluation and care.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is a metastatic brain tumor curable?
Complete cure remains difficult in many cases, but treatment can control growth and relieve symptoms.
2. Which cancers spread to the brain most often?
Lung, breast, melanoma, kidney, and colorectal cancers commonly spread to the brain.
3. What is the first sign of brain metastasis?
Headaches, seizures, or sudden neurological changes often appear first.
