Banana: Nutrition, Benefits & Healthy Eating Guide
Banana ranks among the most consumed fruits worldwide. The scientific name is Musa spp. People love it because it is affordable, widely available year-round, and packed with natural nutrients. Soft texture, pleasant sweetness, and quick energy make bananas suitable for all ages—from children to adults.
Key Characteristics
Soft texture and naturally sweet flavor
Easily digestible
High potassium and carbohydrate content
Supplies instant energy
Raw or ripe—both forms are edible
Often preferred during stomach discomfort
Top Producing Regions
India grows the highest volume of bananas globally.
Other major producing countries include:
China
Indonesia
Philippines
Brazil
Within India, high production comes from:
Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra, Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, and Assam.
Nutrition Facts (Per 100 g)
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
| Nutrient | Amount per 100 gram |
|---|---|
| Calories (Kcals) | 60 kcal |
| Water (g) | 83–85 g |
| Protein(g) | 0.8 g |
| Total Fat (g) | 0.4 g |
| Carbohydrates(g) | 15 g |
| Glucose(g) | 2.0–3.0 g |
| Potassium (mg) | 168 mg |
| Calcium (mg) | 11 mg |
| Iron (mg) | 0.2 mg |
| Magnesium (mg) | 10 mg |
Health Benefits
✔ Instant Energy Source
Natural sugars and carbohydrates help boost stamina during physical activity.
✔ Supports Digestion
Dietary fiber promotes better bowel movement and reduces constipation.
✔ Heart and Nerve Support
Potassium helps maintain nerve function and healthy blood pressure.
✔ Gentle on the Stomach
Many people tolerate bananas well during acidity or gastric discomfort.
✔ Helps Restore Electrolytes
Potassium supports fluid balance after sweating or dehydration.
Daily Recommended Quantity
Most adults can eat:
👉 1–2 medium bananas daily.
Large portions may increase sugar and carbohydrate load.
Best Ways to Eat
Ideal as a morning breakfast or mid-meal snack
Effective pre- or post-workout for energy recovery
Works well when combined with oats, yogurt, or chia seeds
Overripe bananas fit well in smoothies—avoid adding sugar
Who Should Be Careful?
Some individuals need controlled intake:
Kidney disease requiring monitored potassium levels
Diabetes—portion control advised
Banana allergy
Extremely ripe bananas may raise blood sugar faster
(Those with medical conditions should seek professional guidance.)
Conclusion
Banana offers essential nutrients, natural sweetness, easily digestible energy, and wide availability. A balanced daily intake supports digestion, stamina, and overall health. People with diabetes, kidney issues, or allergies should eat bananas mindfully to avoid complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How many bananas are safe to eat per day?
Generally, it is safe and beneficial for an adult to eat 1-2 medium-sized bananas per day. They are a good source of energy, fiber, and potassium. However, those with certain health conditions (such as kidney disease or diabetes) may want to reduce the amount.
2. Can diabetics eat bananas?
Diabetics can eat bananas, but in small amounts and in moderation. Bananas contain natural sugars, so eating too many at once can raise blood sugar. Eating the whole fruit is safer than juice.
3. When is it most beneficial to eat bananas?
Eating bananas is beneficial in the morning with breakfast, before exercise, or when you need a quick energy boost. Fiber and carbohydrates provide energy to the body. It is best not to eat too much before going to bed at night.
Related Posts
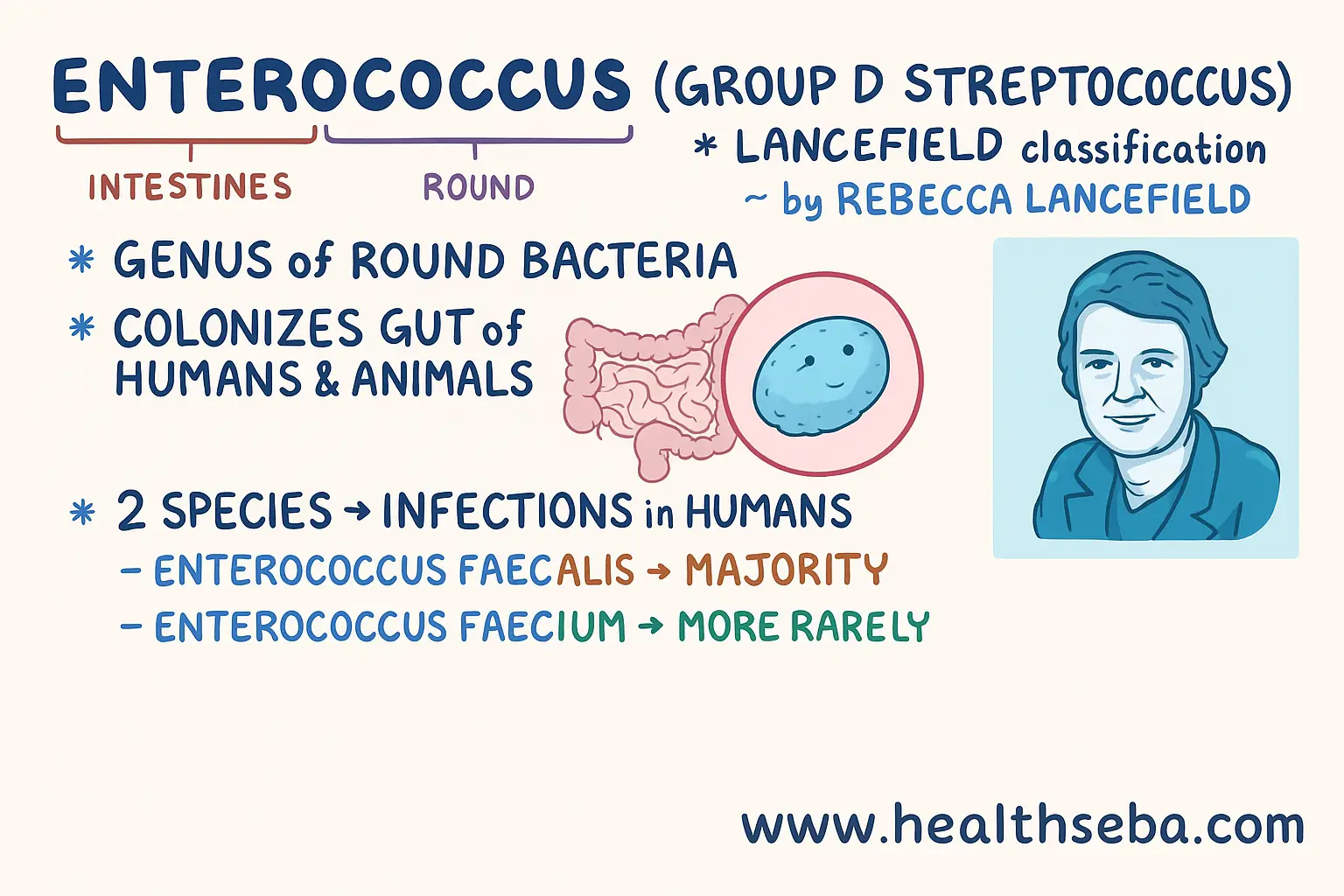
Enterococcus
Enterococcus Introduction Enterococcus is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria. At…
Histopathology Staining
Introduction Microscopic tissue evaluation depends on color contrast to identify…